CISDI’s quest to develop innovative green hydrogen metallurgy
Date:2021/4/25 Source: CISDI
The global steel sector is phasing out the use of fossil fuels and turning to hydrogen and other zero-carbon energies in its commitment to developing greener manufacturing methods.
A number of countries searching for innovative solutions to decrease the CO2 emissions of their steel production have already set out their hydrogen metallurgy plans and lab-scale projects.
The EU’s ULCOS project, the Nordic countries’ HYBRIT, Germany’s SALCOS and Japan’s COURSE50 projects are based on hydrogen-rich blast furnace ironmaking, hydrogen-based DRI and water electrolysis with clean energy power generation. These routes have not yet been commercialised or industrialised.
CISDI first set out its plans to research new processes for low-carbon smelting in 2008.
A number of technological developments have now been achieved in all-oxygen, hydrogen-rich blast furnace ironmaking, gas circulation, gas-based shaft furnace and green electric arc furnace melting.
These developments are enriching global low-carbon tech routes and underpinning our endeavours for innovation-driven advancements.
CISDI’s tech route for hydrogen metallurgy
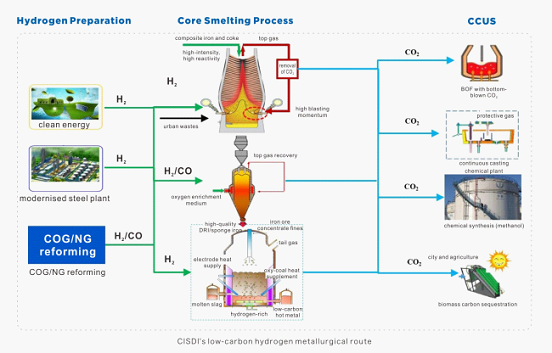
The keynote of CISDI’s low-carbon hydrogen metallurgical route is hydrogen preparation – hydrogen metallurgy – carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS).
Its theoretical research and applied process and equipment is focussed on three major technologies –
ü Hydrogen-rich, low-carbon blast furnace
ü Gas-based direct reduction shaft furnace
ü Hydrogen-based smelting reduction.
The following chart shows CISDI’s low-carbon hydrogen metallurgical route:
Ongoing research and development
CISDI has linked up with China’s universities to conduct hydrogen-injected blast furnace internal mechanism tests and study the critical tech for coke and iron ore KPI matching, the blasting moment with approximate blast furnace conditions and the raceway control.
Since 2014, CISDI has led China’s first research programme for a gas-based shaft furnace - melting separation electric arc furnace, a new tech and equipment.
This programme has led to the creation of a proprietary shaft furnace design and an efficient, safe control system based on a mastery of the H, C, Fe and O systematic interactions, gas-flow uniform distribution unit, optimised furnace profile and long-service-life, reliable refractory arrangement.
CISDI has been consistently involved with COREX-3000 phase I and II’s design, construction and operation.
Its endeavours have laid a strong foundation for CISDI to progress in hydrogen metallurgy.
Forming a hydrogen metallurgy league
CISDI has formed an alliance with four leading Chinese companies to create a hydrogen metallurgy strategic league.
The league has pledged to work closely together to develop hydrogen injection into the blast furnace ironmaking process and hydrogen shaft furnace tech.
A demo hydrogen metallurgy project for steel-chemical co-production is also a major future goal.

CISDI’s four fellow members – Tianjin Rongcheng United Steel, the Northeastern University, Sinopec Tianjin and Shaanxi Blower Group - are pictured at the league’s inauguration ceremony
Commitment to net zero emissions
In addition to joining the global collaboration on hydrogen metallurgy routes, CISDI has built its own technical parameters and evaluation system for hydrogen preparation, feedstock, ironmaking and steelmaking procedures, based on its studies on resource, energy, environmental protection and policy from different regions.
A tech route green assessment system has also been formulated at CISDI with Monte Carlo simulation and net present value methods. This system focuses on multiple factors and various targets for drawing up pertinent tech routes to differentiated resource allocations, energy utilisations, economic behaviours and environmental impacts.
Taking into account China’s steel tech level and its carbon emission status, CISDI has laid down its net zero emissions roadmap:
ü By 2030, a 35 per cent or more reduction in CO2 emissions via hydrogen-rich, low-carbon blast furnace ironmaking tech;
ü Over 60 per cent reduction of CO2 emissions by hydrogen-based direct reduction tech by 2030;
ü Attempts to achieve net zero emissions via CCUS tech in the distant future.

